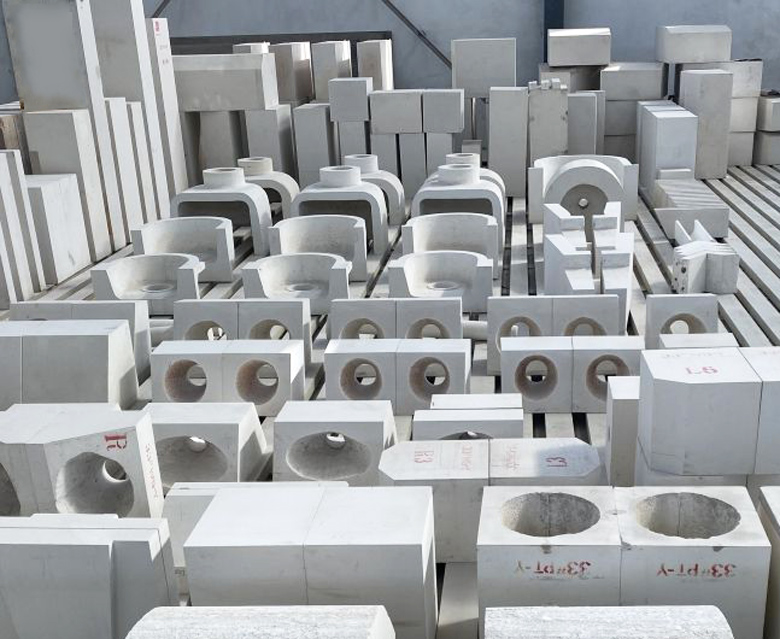
AZS refractory bricks, scientifically known as fused cast zirconia corundum bricks, are produced by completely melting the raw materials and casting them into molds, where they cool and solidify. They are primarily used in glass furnaces. During production, the casting methods vary depending on the application scenarios and specific locations within the furnace.
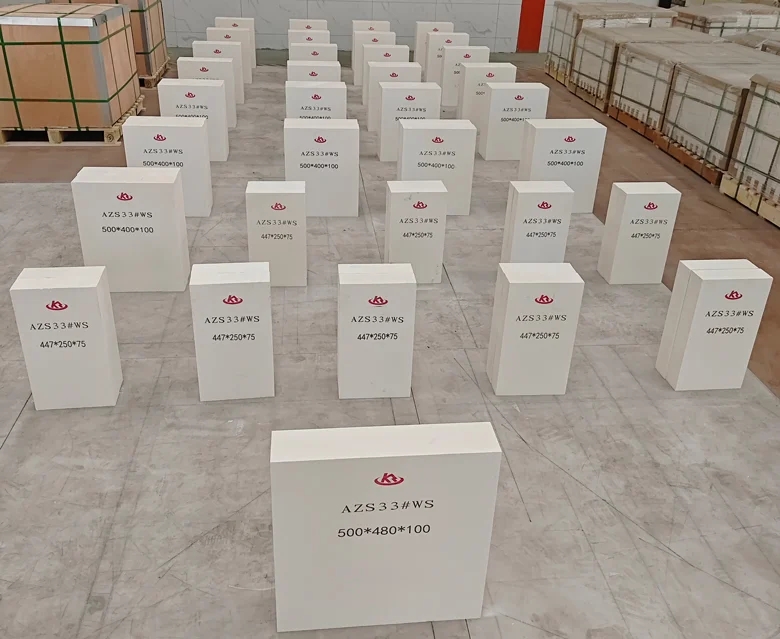


Types of AZS Brick Casting Methods
The production process of AZS bricks mainly consists of several stages: raw material formulation, high-temperature melting, casting, and cooling. Among these stages, casting is the crucial step that determines the shape and internal structure of the brick.
Based on the different casting methods, AZS bricks can be classified into: ordinary casting, tilt casting, quasi-void-free casting, and void-free casting. Currently, the most commonly used method is the electric melting method for ordinary casting. Different casting techniques for AZS products can meet the operational requirements of various parts of ceramic melting kilns, soda ash kilns, and glass furnaces. These bricks are resistant to erosion, corrosion, and have a long service life.
Type 1. Ordinary Casting (PT)
This is the most common casting method, where molten AZS liquid is directly poured into molds.
Location of Shrinkage Cavity: The shrinkage cavity is typically located at the lower part of the pouring gate.
Applications: This method is suitable for the upper structures of melting tanks and areas with moderate erosion.
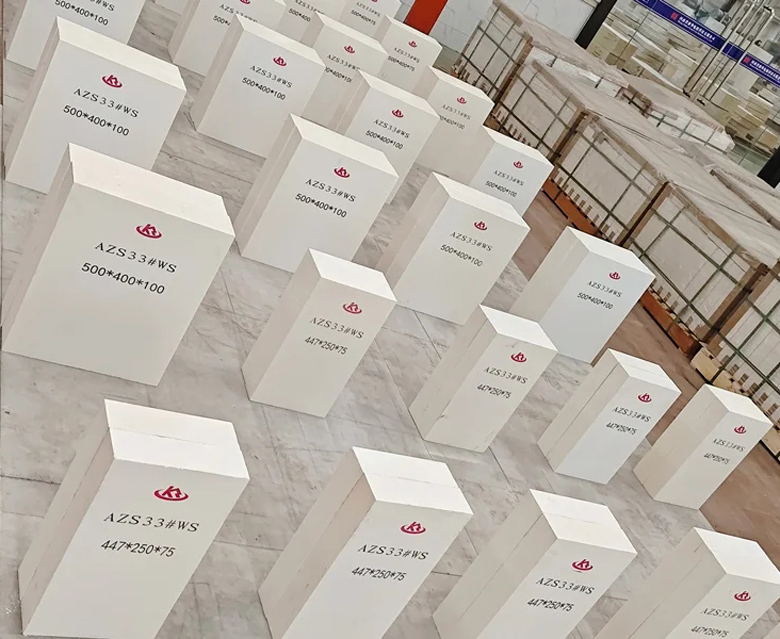
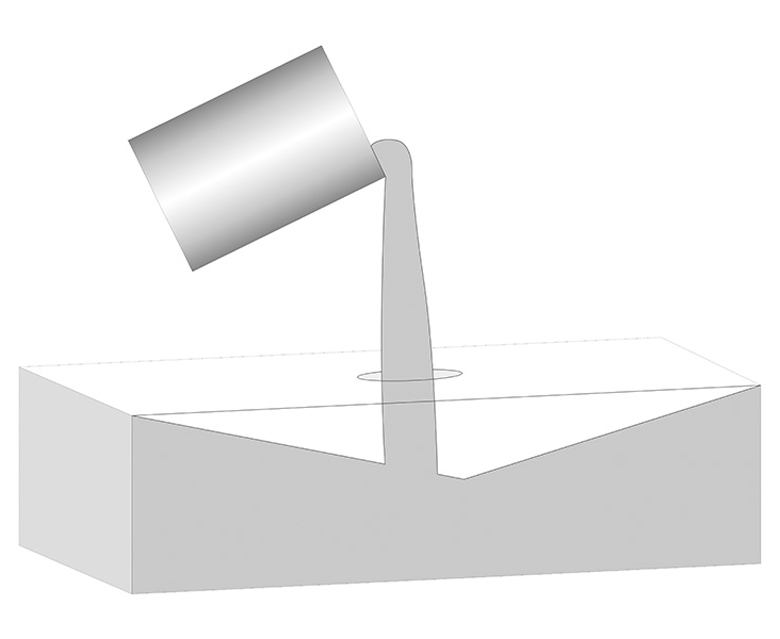

Type 2. Tilt Casting (QX)
By tilting the mold, the shrinkage cavity is shifted to the lower end of the brick. In tilt casting, the shrinkage cavity is concentrated at one end, while the other end remains very dense. The tilt angle is typically between 30° and 35°.
Applications: This method is primarily used for wall bricks in melting tanks, as it effectively reduces the impact of shrinkage cavities on the strength of the tank walls.
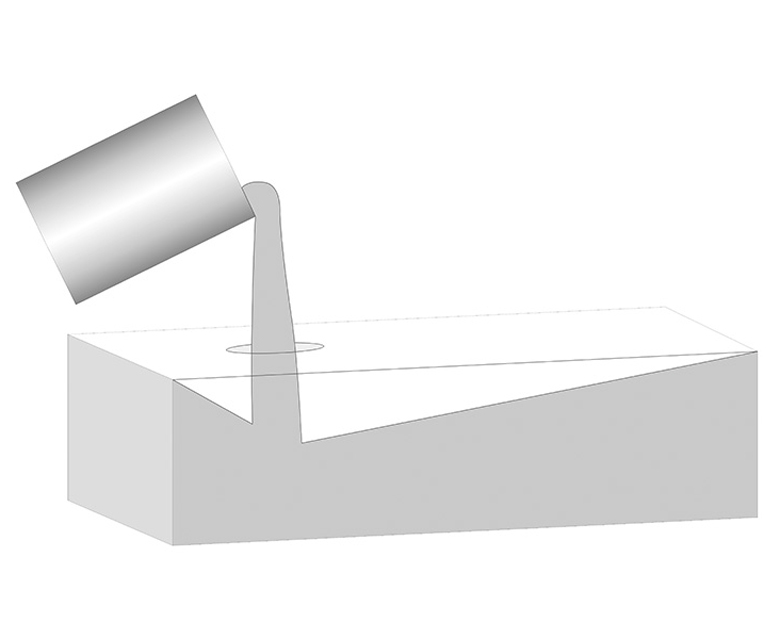

Type 3. Quasi-Void-Free Casting (ZWS)
This method employs vertical casting, where the cast dimensions are larger than the required size. After annealing, the upper portion containing shrinkage cavities is largely removed.
Applications: This method is suitable for wall bricks in melting tanks and other areas that require higher density in glass industry.
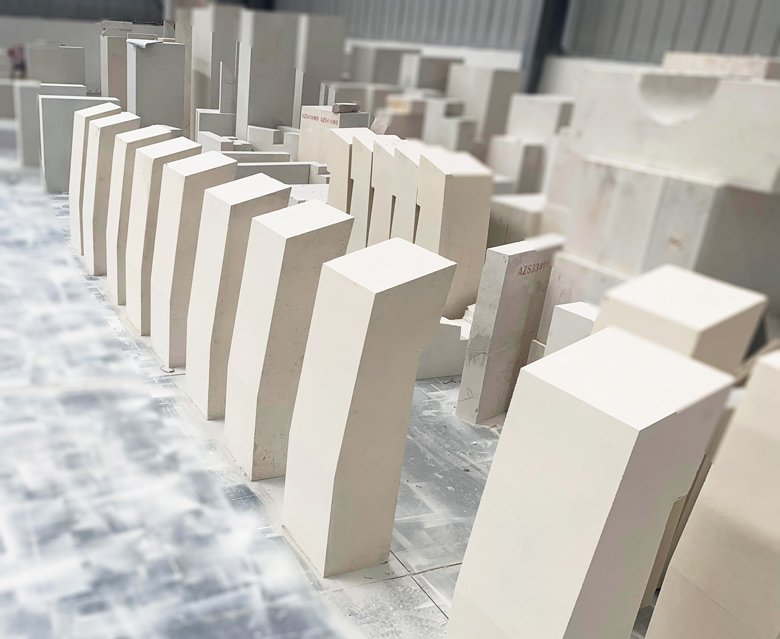
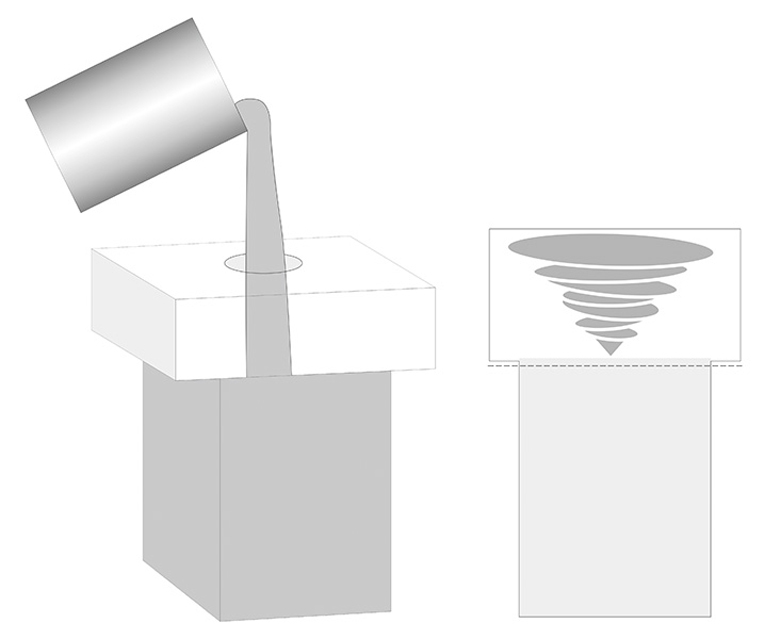

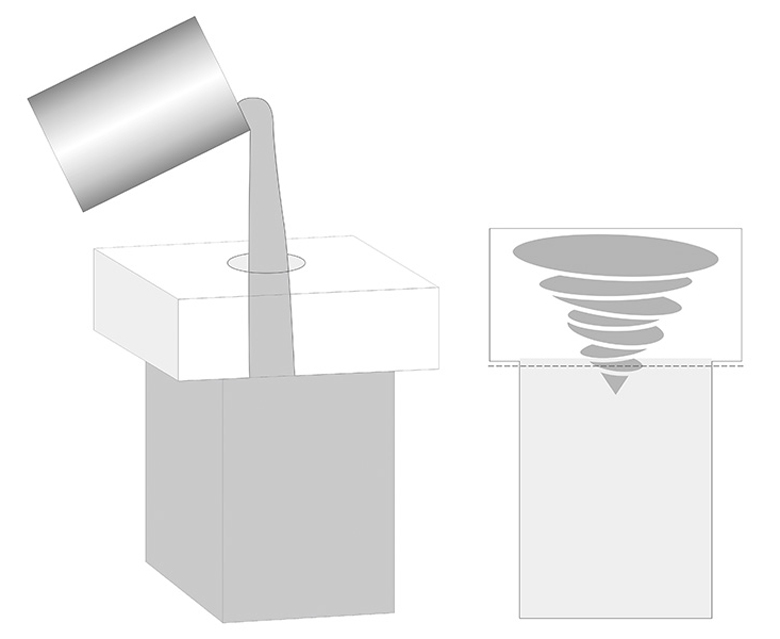
Type 4. Void-Free Casting (WS)
This method uses vertical casting, where the cast dimensions are larger than the required size. After annealing, the upper portion containing shrinkage cavities is removed, resulting in a very dense structure. Void-free casting has a higher cost but offers better performance.
Applications: This method is suitable for areas with severe erosion, such as liquid holes, kiln shelves, corners of melting tanks, and paving.

Impact of Different Casting Methods on the Performance of AZS Bricks
- Location of Shrinkage Cavities: The position of shrinkage cavities can affect the strength and thermal shock resistance of the bricks.
- Density: Different casting methods influence the density of the refractory bricks, which in turn affects their wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
- Porosity: The porosity of the bricks impacts their thermal conductivity and thermal shock resistance.
Selection of Casting Methods
Choosing the appropriate casting method requires a comprehensive consideration of the following factors:
- Application Location: Different locations have varying requirements for the bricks, such as the top of the melting tank, tank walls, and liquid holes.
- Operating Conditions: Conditions such as temperature, atmosphere, and corrosiveness will also influence the selection of bricks.
- Performance Requirements: Considerations for performance requirements, including strength, density, and thermal shock resistance.
How to Choose the Appropriate Casting Method for AZS Bricks?
- Select Based on Application Location;
- Select Based on Operating Conditions: Consider factors such as temperature, atmosphere, and corrosiveness;
- Select Based on Performance Requirements;
- Consider Economic Factors: Take into account overall cost-effectiveness.
The selection of casting methods for AZS bricks is a systematic project that requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors. By making scientifically sound choices, it is possible to effectively enhance the service life and production efficiency of kilns. Kerui Refractory can provide you with comprehensive solutions and guidance. If you have any needs, please feel free to contact us.



